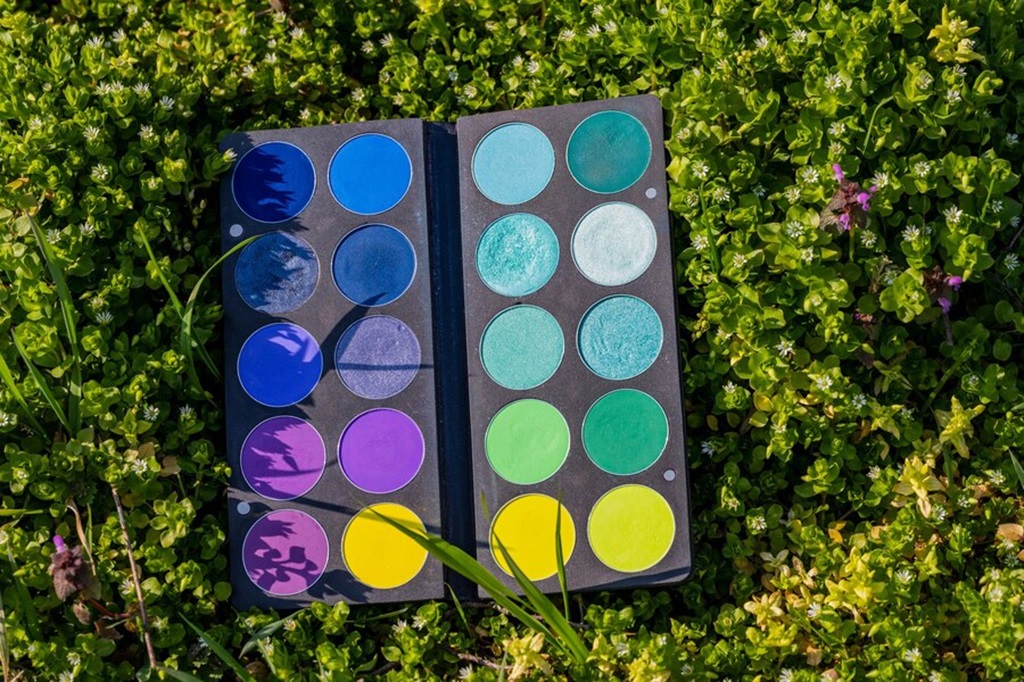
Have you ever wondered, what color does blue and green make? This question combines the mysteries of art, science, and perception into a vibrant exploration. When blue and green collide, the result is not only a mesmerizing color but also an opportunity to understand how hues interact in the world of pigments and light. Whether you’re an artist, designer, or curious mind, uncovering this blend provides a lens to see the world differently.
Interestingly, when exploring the interplay of blue and green, the result is often described as cyan or teal—colors with unique psychological effects and applications in design. To delve deeper into color theory, explore ldphub, a treasure trove of artistic knowledge.
In this article, we’ll analyze the science behind color mixing, the cultural and psychological interpretations of cyan-like hues, and how they are applied in various fields. Let’s blend logic with creativity to unveil the secrets of this mix.
Understanding the Basics of Color Theory
Primary Colors and Their Role
Colors stem from the three primary hues: red, blue, and yellow. From these, secondary colors are formed by mixing two primaries, such as blue and yellow creating green. However, blending secondary and primary colors leads to tertiary hues—complex shades like cyan, which often arises when blue and green meet.
Additive vs. Subtractive Color Mixing
To understand what color blue and green make, we must address the two dominant methods of color mixing:
- Additive Mixing: Used in light, as seen on screens. Mixing blue and green light creates cyan.
- Subtractive Mixing: Applied in pigments or paints. Here, blue and green create a muted turquoise, as pigments absorb certain wavelengths while reflecting others.
Statistics reveal that additive color mixing, used in digital spaces, represents 80% of visible media interactions, emphasizing its modern relevance.
The Result: What Color Does Blue and Green Make?
When blue and green meet, the resulting color leans towards cyan, teal, or turquoise, depending on the medium and ratios. Let’s explore these hues in more depth.
Cyan: The High-Energy Result
In additive color mixing, cyan is produced when equal parts blue and green light combine. This color is often associated with high energy and freshness, making it a favorite in marketing and tech. For example, brands like Twitter use cyan to evoke trust and innovation.
Logic Behind Cyan:
- Scientific Basis: Cyan reflects a wavelength between blue and green (490–520 nm), providing a sense of calm and clarity.
- Psychological Impact: According to color psychology, cyan promotes communication and focus, which is why it’s prevalent in tech and healthcare.
Turquoise: The Painter’s Delight
In subtractive mixing, blue and green often yield turquoise, a versatile shade balancing the tranquility of blue and the vitality of green. Turquoise is popular in art and fashion for its soothing yet energizing aesthetic.
To learn more about this process, check out how to make turquoise color, where practical tips on achieving this shade await.
Opinions on Turquoise:
- Artists’ Perspective: Many artists view turquoise as a “bridge” color, perfect for transitioning between cool and warm tones in their work.
- Designers’ Take: Interior designers often recommend turquoise for spaces requiring a serene yet uplifting vibe, like spas or home offices.
Why Blue and Green Combinations are Iconic
Nature’s Palette
Nature itself showcases the blend of blue and green magnificently. From tropical oceans to lush forests, this combination symbolizes vitality and serenity. It’s no wonder why humans find cyan and turquoise hues so appealing.
Fun Fact:
Studies indicate that humans perceive blue and green hues as the most calming on the spectrum, explaining their frequent use in meditation and mindfulness spaces.
Cultural Significance
Across cultures, cyan and turquoise hold distinct meanings:
- Ancient Egypt: Turquoise represented protection and prosperity.
- Modern Branding: Cyan is a key part of minimalist, clean design trends dominating today’s tech landscape.
Related: A Burst of Sunshine: Exploring the World of Yellow Spray Paint
How to Achieve the Perfect Blend of Blue and Green
Mixing Tips for Beginners
Achieving the ideal cyan or turquoise shade depends on several factors:
- Pigment Ratios: Use more blue for a cooler tone or more green for a warmer effect.
- Lighting Conditions: Experiment under natural and artificial lighting to see the true color.
- Medium Choice: Watercolor, acrylic, and digital mediums can all affect the outcome.
Cyan and Turquoise in Modern Design
Digital Applications
From UX design to app development, cyan and turquoise are prominent in digital spaces. These colors not only enhance readability but also evoke a sense of professionalism and creativity.
Case Study:
Tech giants like Google integrate cyan into their interfaces to create a user-friendly, inviting atmosphere.
Fashion and Interior Trends
Turquoise has seen a resurgence in both fashion and interior design, representing a modern take on retro aesthetics. Fashion houses and influencers alike have adopted turquoise as a statement color for its versatility.
Related: Can you paint over redguard?
The Psychology Behind Cyan and Turquoise
Emotional Effects
These hues are linked to both calming and energizing qualities, making them ideal for reducing stress while maintaining focus.
Health and Wellness
Research suggests that exposure to cyan and turquoise lighting can improve mood and cognitive performance, a technique increasingly used in therapeutic settings.
Conclusion: Unlocking the Beauty of Blue and Green
So, what color does blue and green make? The answer lies in their harmonious blend, producing mesmerizing shades like cyan, teal, or turquoise. Whether you’re painting a masterpiece, designing a website, or simply observing nature, understanding this mix opens doors to creativity and innovation.